The Gaming Industry: A Privileged Target for Crooks — The Fortnite Case
Introduction
In the past, we've reported many cases of cyberattacks against companies operating in the gaming industry. We observed many attacks, especially DDoSing, against the infrastructure behind the most popular gaming consoles. In other cases, hackers targeted gaming forums to steal sensitive data for phishing attacks against the gaming community.
The popularity of some games can attract cybercriminals that attempt to scam its gamers with various tricks. This is what is happening with one of the most popular games today, Fortnite.
Android Users: Don't Install Fortnite Android APK
Fortnite is currently one of the most popular games available, and crooks are attempting to exploit the interest in the forthcoming Fortnite Android to infect millions of fans.
Fortnite is a co-op sandbox survival game developed by Epic Games and People Can Fly. It was released as a paid-for early access title for Microsoft Windows, macOS, PlayStation 4 and Xbox One on July 25, 2017, with a full free-to-play release in 2018.
The Fortnite game today has more than 125 million active users, all potential targets of cybercriminals who are already attempting to exploit its popularity and target the fans.
Unfortunately for Android users, Fortnite for Android devices is not yet available. The authors are currently developing it; the iOS version was already released in March by Epic Games. According to the company, the Battle Royale game is planned to be released for Android devices this summer.
But in recent weeks, cybercriminals attempted to take advantage of Android users' interest in an alleged version for Android version of the popular game.
Searching for the Fortnite Android version online, it is quite easy to find blog posts and video tutorials with instructions to install a fake Fortnite Android App.

Figure 1 - Fake Fortnite Android App
Searching for the 'Fortnite Android App' on YouTube you will get a high number of videos on "How to install Fortnite on Android." Many of these videos were viewed millions of times, and some of them also include links to actual Fortnite APK files.
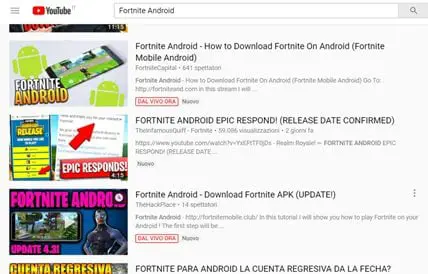
Figure 2 - Fake online tutorials
The high interest in the alleged Fortinet Android app is confirmed by data provided by Google Trends that shows a growing number of users searching for the term "Fortnite Android."
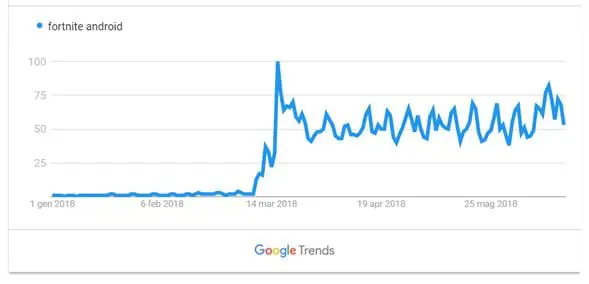
Figure 3 - Google Trends for Fortnite Android
Hackers are exploiting this interest to trick Android fans into downloading tainted versions of the game that can compromise Android devices.
Many video tutorials published on YouTube and shared in some gaming forums provide instructions on how to "install a few other apps" to unlock the Android Fortnite game. These apps could hide malicious code such as cryptocurrency miners or adware that allow attackers to generate revenue.
The malware researcher Lukas Stefanko (@LukasStefanko) claims that videos on "How to install Fortnite on Android" have obtained millions of views on YouTube.
An impressive number of links purport to be official Fortnite app downloads are used by crooks to deliver malicious applications.
If you are a fan of the Fortnite game, you have to wait until next summer for the official Android version. In the meantime, don't install alleged beta versions of the popular game from third-party stores.
Even if you see the Fortnite Android version in the official Google Play store, do not download it.
Fortnite Players Infected by Adware
Not only Android users interested in Fortinite app are targeted by cybercriminals. Crooks are now targeting gamers searching for a Fortnite v-bucks generator.
A v-buck is the in-game currency that can be spent in both the Battle Royale PvP mode and the Save the World PvE campaign — in the former to purchase new customization items, while in the latter to purchase Llama Pinata card packs.
V-bucks can be purchased with credit card or other electronic systems, such as PayPal, but many gamers search for v-buck generators to obtain them for free.
Unfortunately, most of these applications hide a malicious code.
Researchers at the Web-based game-streaming platform Rainway recently reported that tens of thousands of Fortnite players have already attempted to download the fake generators with the result of infecting their systems.
The malicious code associated with this campaign is a strain of malware that hijacks encrypted HTTPS web sessions to inject fraudulent ads into every website visited by the users.
"On the early morning of June 26th, we began receiving hundreds of thousands of error reports to our tracker. Not feeling very excited to see such an influx of events on a Tuesday the engineering team was a bit flustered, after all, we hadn't released any updates to that particular piece of our solution." -Rainway CEO Andrew Sampson
The experts at Rainway started the investigation after they noticed hundreds of thousands of error reports from server logs. The experts at the company discovered that the systems of their users were attempting to connect with various ad platforms.
Since Rainway's system only allows users to load content from whitelisted domains, all the connection errors observed by the company were generated by requests to download ads from blocked domains.
Rainway researchers decided to conduct further analysis and to identify the code responsible for these connections to unauthorized websites. They analyzed hundreds of Fortnite exploit programs, searching for the ones that were generating the same errors reported by Rainway users.
The experts discovered that the errors were generated by systems infected with a fake v-bucks generator.
Searching online, it is quite easy to find any kind of software that poses as a Fortnite hack tool. These applications are advertised through YouTube videos and claim to allow players to generate free v-bucks, in addition to a classic aimbot.
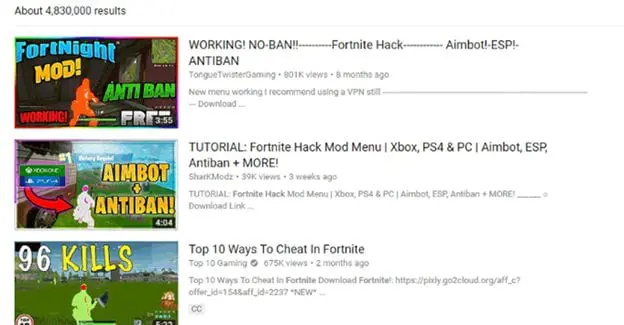
Figure 4 - Fortnite hack tools advertisement
Once the malicious code has infected the player's system, it will immediately install a root certificate and configure the Windows machine to act as a proxy for the web traffic and to inject ads.
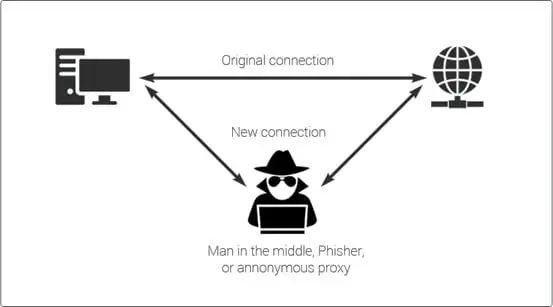
Figure 5 - Fortnite campaign
The Rainway experts identified the servers hosting the malicious code used in the campaign. They were legitimate machines that were compromised by attackers.
Rainway informed the companies operating the compromised servers, and some of them quickly removed the malware.
"Now, the adware began altering the pages of all web request to add in tags for Adtelligent and voila, we've found the source of the problem — now what?
"We began by sending an abuse report to the file host, and the download was removed promptly, this was after accumulating over 78,000 downloads. We also reached out to Adtelligent to report the keys linked to the URLs. We have not received a response at this time. SpringServe quickly worked with us to identify the abusive creatives and remove them from their platform." -Rainway.
Rainway is warning gamers to not to install hack tools or game cheats.
Conclusions
Given Fortnite's popularity, we can imagine that many other cases will emerge in the forthcoming weeks. Similar attacks could be observed against other gaming communities. In fact, there have already been previous instances of such attacks: in January 2017, a fake Super Mario Run for Android was spotted serving the Marcher banking Trojan.
Sources
Don't install Fortnite Android APK because it could infect your mobile device, Security Affairs
Adware already infected at least 78000 Fortnite Players, Security Affairs

Get your guide to the top-paying certifications
With more than 448,000 U.S. cybersecurity job openings annually, get answers to all your cybersecurity salary questions with our free ebook!
How We Discovered a Virus Infecting Tens of Thousands of Fortnite Players, Rainway










